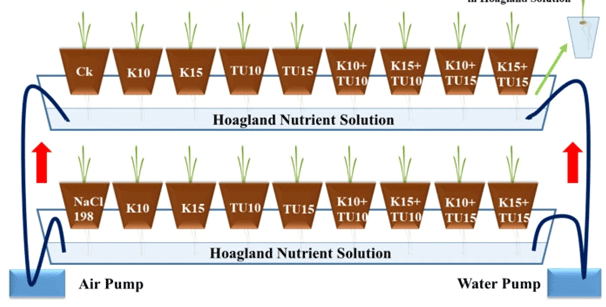
This research explores innovative solutions to combat salt stress in wheat cultivation, presenting a breakthrough combination of potassium and thiourea that significantly mitigates the adverse effects of salinity on crop growth and productivity.
Salt stress poses a severe threat to agricultural productivity worldwide, particularly affecting wheat crops. This study investigates the mechanisms of salt stress impact and proposes an effective mitigation strategy using potassium and thiourea.
Mechanisms of Salt Stress
Salt stress disrupts plant growth through multiple pathways:
- Imbalance of ionic equilibrium
- Induction of oxidative stress
- Compromised cellular integrity
- Inhibition of chlorophyll biosynthesis
- Reduced photosynthetic efficiency
The Protective Role of Potassium and Thiourea
The combined application of potassium and thiourea demonstrates remarkable protective effects:
- Enhanced chlorophyll synthesis
- Reduced oxidative damage
- Preserved cellular integrity
- Improved water balance regulation
- Stimulated antioxidant enzyme activity
Scientific Validation
The efficacy of this approach is supported by positive correlations between:
- Growth parameters
- Antioxidant enzyme activity
- Gas exchange characteristics
- Chlorophyll content
Practical Implications
The findings suggest that potassium and thiourea can serve as:
- Cost-effective soil conditioners
- Environmentally friendly solutions
- Sustainable tools for salinity management
- Yield-enhancing agents in saline conditions